
by Baginda Tirtadji | Friday, March 11, 2022 | Breathing, Research
When you’re not sleeping well, does anything else matter? There’s nothing more frustrating than lying awake at night watching the clock.
One secret to achieving more restful slumber? Focus on achieving a healthy breathing rate while you sleep.
Most of us don’t spend too much time wondering whether our vital signs are in the normal range, but if you’re struggling to get quality sleep, it’s time to take a look. Our vital signs include measurements of health like blood pressure, pulse rate, and breathing rate (also known as your respiratory rate). Your breathing rate refers to how many times you breathe in a minute.
When your breathing rate during sleep becomes too fast or too slow, you may find that it’s hard to stay asleep. You might also wake up feeling tired.
Why? Because our breathing is closely linked with our sleep quality.[*] To start getting more restorative sleep, take a deep breath and read on.
For anyone looking to improve their sleep, Somnox 2 is your science-backed sleep companion that guides you towards slow-paced breathing that helps you fall asleep faster, worry less and wake up rested. 70% of our users improved their sleep quality within 4 weeks. Interested?
How We Breathe During Sleep
A number of changes take place in our bodies when we sleep, including how we breathe. First, our breathing rate tends to slow down and become more constant during periods of rest and sleep. This is because our metabolic rate decreases during sleep, and a slower metabolic rate leads to slower breathing. Our other vital signs like heart rate and blood pressure go down during sleep as well.[*]
Our muscles also relax during sleep, including our respiratory muscles. The result is a slower breathing rate because the muscles around the lungs are not working as hard as they normally do when we are awake.[*]
The stage of sleep also affects our breathing rate during sleep. Most of us experience fragmented sleep with different phases and awakenings throughout the night. There are 4 stages of sleep, and our breathing changes as we enter each one.
Non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep is divided into 3 stages, and the breathing rate is typically constant. During stages 1 and 2, our bodies are in a state of light sleep, and the heart rate begins to decrease. As we enter NREM stage 3, our bodies relax more fully, and breathing starts to slow down. During rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, our brains become more active, and breathing tends to be more irregular. The average breathing rate during REM sleep is usually a bit lower than in NREM sleep or wakefulness.[*]
What’s a Good Breathing Rate During Sleep?
Healthy vital signs like your respiratory rate during sleep vary with age and health. For adults, a good breathing rate at rest is 12 to 20 breaths per minute.[*]
A 2016 study found that the average breathing rate for adults without a respiratory condition was about 15 to 16 breaths per minute. This was true in all phases of sleep including both REM and NREM. In this study, the breathing rate during sleep was only slightly slower than the average awake breathing rate of 17 breaths per minute.[*]
How to Measure Breathing Rate During Sleep
You may be curious about your own breathing rate during sleep. How can you know if you’re in the healthy range? There are a few different ways for adults to measure respiration during sleep, including:
- Manual counting: One way to measure your breathing rate during sleep is for your partner or friend to watch you while you rest (sounds creepy but it works). By counting how many times your chest rises and falls in a minute, they can measure your respiration rate.
- Wearable devices: Smartphones, smartwatches, and other wearable devices can be worn at night to measure your breathing rate during sleep and notify you of any irregularities.[*]
- Smart Breathing technology: The Somnox 2 monitors your breathing rate overnight and responds to your breathing in real-time, actively slowing down your breathing rate and helping you to calm down.
Conditions that Lead to Abnormal Respiration
Several chronic health conditions can affect your breathing rate during sleep. It’s important to know the warning signs.
- Obstructive sleep apnea: This type of disordered breathing occurs when the upper airway becomes blocked during sleep.
- Central sleep apnea: Individuals with central sleep apnea experience paused breathing during sleep because their brains do not send the message to the respiratory muscles that it is time to breathe.
- Cardiovascular disease: Research shows that individuals who have or are at risk of cardiovascular disease are more likely to experience disordered breathing during sleep.[*]
- Asthma: When individuals with asthma lie flat on their backs during sleep, their lung capacity goes down significantly. This makes it difficult for the body to sustain a normal breathing rate during sleep.[*]
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): COPD refers to a group of chronic lung conditions that block airflow to the lungs.
- High body mass index (BMI): Having a high BMI has been linked to a higher risk of sleep apnea.[*]
- Mental health: Irregular breathing during sleep has been linked with mental health challenges like anxiety and depression. A 2015 study found that sleep apnea may raise the risk of developing a panic disorder.[*]
- Pneumonia: Pneumonia is a lung infection that causes the air sacs in the lungs to become inflamed. This makes breathing more difficult and lowers one’s lung capacity.[*]
- Narcotic use or abuse: Narcotic medications cause our respiratory rate to slow down and become more shallow. This is especially true during sleep.[*]
When Should I Talk to My Doctor?
Good sleep is vital to your health and quality of life. If you experience any of the following symptoms during or after sleep, consider discussing them with yourdoctor:[*]
- Snoring every night
- Restless sleep
- Morning headaches
- Chronic fatigue
- Trouble remembering or thinking clearly throughout the day
Tips for Healthy Respiration During Sleep
A healthy breathing rate is essential to getting restorative sleep. Fortunately, there are simple steps that you can start taking tonight to improve your quality of sleep (and life!).
To improve your breathing rate while you sleep, try incorporating one or more of the following tips:
- Sleeping position: Sleeping on your side can increase your lung capacity and improve your breathing pattern.[*]
- Avoid allergens: To improve the air quality in your bedroom, consider investing in an air purifier to remove bacteria and allergens from your environment.[*]
- Breathing support: To deepen and improve your breathing rate during sleep, try the Somnox 2 (it breathes with you!).
For anyone looking to improve their sleep, Somnox 2 is your science-backed sleep companion that guides you towards slow-paced breathing that helps you fall asleep faster, worry less and wake up rested. 70% of our users improved their sleep quality within 4 weeks.

by Baginda Tirtadji | Friday, March 11, 2022 | Breathing, Research
Take a deep breath and see how you feel. If you notice your muscles relaxing and your thoughts slowing down, there’s a reason for that. Deep breathing has several health benefits that can lift your mood and improve your quality of life.[*]
Performing deep breathing exercises is a simple way to start taking care of your health. When you have a chronic health condition or simply want to make some improvements, it can be overwhelming to know where to start.
Start with deep breathing. It’s free, can be done at any time, and doesn’t have side effects like medications. To start easing stress and improving your health, read on to learn the health benefits of deep breathing.
What Is Deep Breathing?
Deep breathing, also known as diaphragmatic breathing, means taking slow, deep breaths on purpose. Diaphragmatic breathing involves the small muscle under the lungs known as the diaphragm.
When you take a deep breath in, the diaphragm contracts and moves down to make room for the lungs to fill with air. When you breathe out and empty the lungs, the diaphragm relaxes and moves back up.[*]
Deep breathing stimulates the vagus nerve, a system of nerves that run from the brain down to the large intestine. The vagus nerve controls involuntary functions in the body like your mood, immune system, digestive system, and heart rate. By stimulating the vagus nerve, deep breathing leads to relaxation and health benefits.[*]
How Deep Breathing Works
Deep breathing allows our bodies to relax because it helps to regulate the sympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for our “fight or flight” response and causes an increase in heart rate, breathing rate, blood pressure, and muscle tension. When the sympathetic nervous system is activated, it’s common to feel irritable and anxious as well.
When you take a deep breath and stimulate the vagus nerve, your parasympathetic nervous system is activated. As opposed to the “fight or flight” response, the parasympathetic nervous system causes a “rest and digest” response. When you trigger this system, your breathing rate, heart rate, and blood pressure all start to come down. You may also notice that you start to feel more like yourself and can think more clearly.
7 Benefits of Deep Breathing
From a better mood to lowered blood pressure, deep breathing can improve your health in a variety of ways.[*]
Relieve Stress
Chronic stress affects just about every aspect of our health. It’s estimated that up to 60% to 80% of patient visits to primary healthcare providers are related to stress. Emotional stress has been linked to a higher number of office visits and incidence of disease.[*]
A 2017 study found that regular deep breathing practices can lead to an overall increased mood and lower stress level. Study participants experienced lower heart rates and cortisol levels after breathing deeply.[*] Cortisol, known as the stress hormone, has been linked with increased levels of inflammation and disease in the body.[*]
Decrease Blood Pressure
Deep breathing has been found to lower blood pressure and help to prevent high blood pressure (hypertension).[*]
A 2019 review found that deep breathing can produce a moderate decrease in blood pressure readings. The researchers suggested that deep breathing could be an effective first step in treating hypertension, especially for individuals who are hesitant to take medication to treat it.[*]
Reduce Irritable Bowel Syndrome Symptoms
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a chronic gastrointestinal condition that causes constipation, diarrhea, stomach pain, and cramping. IBS greatly affects one’s quality of life, and the symptoms can be triggered by stress.
A 2020 study found that a daily deep breathing practice can improve IBS symptoms. The study also found that participants who took part in the deep breathing program reported improved moods and higher quality of life.[*]
Improve Chronic Pain
The way we breathe affects how the brain processes pain signals. Taking deep breaths has been shown to change the way the brain perceives pain and lowers the intensity. Deep breathing can also improve feelings of tension, anger, and depression in those who experience chronic pain.[*]
Improve Posture and Strength
Breathing deeply can help to strengthen the posture muscles in the body. A small 2017 study found that participating in a daily deep breathing program improved the posture of study participants.[*] Sitting upright provides more room for the lungs to breathe, so an improved posture can make breathing deeply feel easier.
Improve Lung Function in Asthma
Asthma is a chronic lung condition that causes the airways to become inflamed and tightened. A 2020 Cochrane review concluded that regular deep breathing exercises can improve lung function in individuals with asthma. Not surprisingly, when people with asthma experienced better lung function, they also reported an increased quality of life.[*] Individuals with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) may experience the same benefits from deep breathing as well.[*]
Improve Cardiac Surgery Outcomes
Deep breathing is an important part of the recovery process after surgery. A 2015 study found daily deep breathing reduces the risk of complications after cardiac surgery.[*]
How to Practice Deep Breathing
Although deep breathing is a simple practice, it takes effort and concentration to do it every day. To get started, find a comfortable place where you can relax and close your eyes. Try lying down and placing one hand on your chest and one hand on your abdomen.
To begin diaphragmatic breathing, first, breathe out to empty your lungs. Next, take a deep breath in through your nose and feel your lungs expanding. If you’re doing it right, you’ll see both your chest and abdomen rise.
Once you have filled your lungs with air, exhale through your mouth (or your nose if you prefer) and notice your abdomen move down again. Try to blow out all of the air in your lungs, and then start again.
While you are practicing deep breathing, you may notice your mind starting to wander. This is normal. Try to avoid judging yourself for this, and simply keep bringing your thoughts back to your breath.
If you could use some more support in your deep breathing practice, consider using the Somnox 2 It breathes with you to help you breathe more deeply and evenly.
To begin a daily deep breathing practice, create a routine that works for you. Set aside a small corner of your home with everything you need. You may want to have a pillow to rest on, a clock or timer to keep track of the time, and the Somnox 2 to help guide your breathing pattern.
As an extra motivational nudge, try setting a reminder on your phone or computer. Aim for one or two sessions per day to start and work your way up from there. Schedule time for deep breathing before bed and any stressful situations throughout the day. Once you develop the habit of deep breathing, you’ll likely notice the benefits right away.

by Baginda Tirtadji | Sunday, February 13, 2022 | Breathing, Research
Breathing is something we do all day and night without even realizing it. In fact, we breathe in and out about 17,000 times a day.[*] Despite being such an inherent part of our existence, many people don’t understand the breathing process or even know why breathing is so essential to life.
In this article, we’ll be taking a deep dive into breathing, exploring how it works and why it’s important, as well as different types of breathing and tips for healthy breathing.
Let’s all take a deep breath—in and out—and get started.
For anyone looking to improve their sleep, Somnox 2 is your science-backed sleep companion that guides you towards slow-paced breathing that helps you fall asleep faster, worry less and wake up rested. 70% of our users improved their sleep quality within 4 weeks. Interested?
How the Respiratory System Works
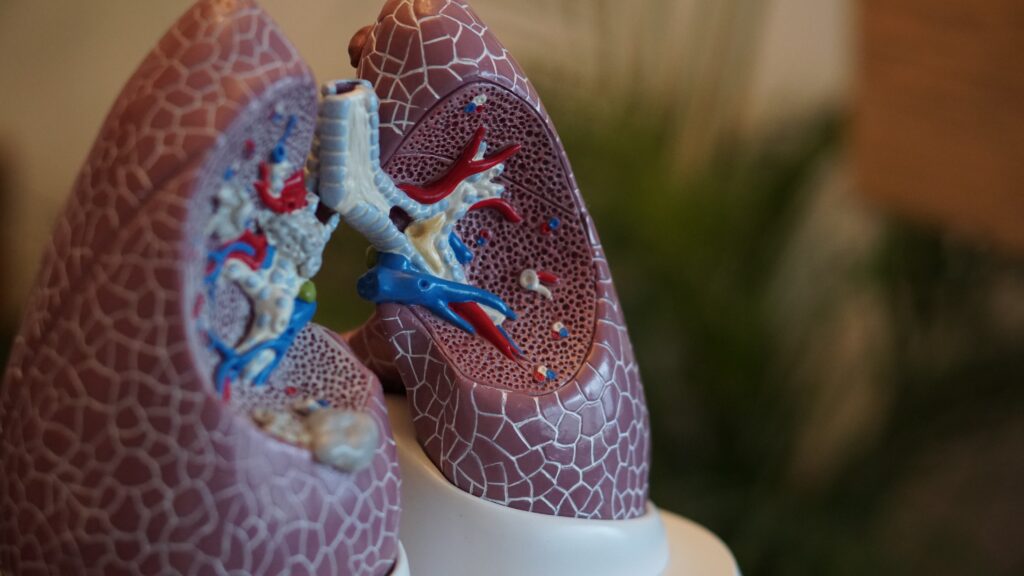
The respiratory system is the network of organs and tissues that allow you to breathe. The two lungs, which sit to the left and right of the heart, are the primary organs of the respiratory system.[*]
The breathing process (aka respiration) has two major phases: inhalation and exhalation. The inhalation process starts when the diaphragm, the muscle located under your lungs, contracts and moves downward. This increases space in your chest cavity, which allows your lungs to expand.
As your lungs inflate, air enters your nose or mouth and travels down your windpipe to your bronchial tubes, which connect your windpipe to your lungs. As the air reaches your lungs, it enters air sacs called alveoli, which pass the oxygen into your bloodstream.
When you exhale, your diaphragm relaxes and shifts up into your chest cavity. As the space in your chest cavity decreases, carbon dioxide-rich air is pushed out of your lungs and windpipe, and then out of your nose or mouth.
How Your Body Controls Breathing
Inhalation is an active process, meaning muscles are involved. Most of the work of inhalation is done by the diaphragm, the main breathing muscle, and to a lesser extent, the intercostal muscles.
Exhalation, on the other hand, is a passive process, meaning no muscle activity is involved. Exhalation is caused by the natural elastic recoil of the lung tissue and is accompanied by the relaxation of all breathing muscles—similar to a balloon deflating.
While you can consciously inhale and exhale at will, breathing is largely an unconscious process that’s controlled by your brain stem.[*] The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord and regulates many automatic bodily processes, including heart rate, blood pressure, reflexes, and breathing.
Your brainstem controls your breathing rate by sensing your body’s need for oxygen, as well as its need to get rid of carbon dioxide, which is a byproduct of cellular respiration.
The Importance of Breathing
Just like food and water, breathing is essential for life. However, while you can go days without water and possibly weeks without food, you can only go a few minutes without breathing.
Why is that? What purpose does breathing serve? The critical nature of breathing is directly linked to the importance of one particular element your body needs every second of every day: oxygen.
Air contains 21 percent oxygen, which you breathe into your lungs.[*] Once inhaled, your lungs pass the oxygen toyour bloodstream, where it’s carried off to your tissues and organs. The cells that make up your tissues and organs then use the oxygen to perform functions that keep you alive.
Breathing also serves as a way to expel carbon dioxide gas, which is a byproduct of cellular respiration.

How Intentional Breathing Can Support Your Body
While breathing is a largely automatic process, you can consciously influence your breathing rate whenever and wherever you’d like.
Intentionally altering your breathing rate allows you to indirectly influence your autonomic nervous system. This is really exciting if you think about it! Consciously slowing your breathing increases the activity of the parasympathetic nervous system (aka “rest and digest”) while reducing the activity of the sympathetic nervous system (aka “fight or flight”).
The parasympathetic nervous system is responsible for the relaxation response and triggers beneficial changes in the body, including a slowed heart rate and reduced blood pressure. When this system is activated, your autonomic nervous system is balanced, which relieves you of anxiety, overwhelm, and restlessness.
In this way, you can use your breath as a tool to calm your body and mind. Research suggests that deep breathing practices can, among other things, soothe anxiety and support restful sleep.[*][*]
To think about it another way, taking deep, diaphragmatic breaths communicates to your brain, “Everything is okay. It’s safe to relax,” in a language it understands.
While diaphragmatic breathing doesn’t require anything but your breath, you can further support your breathing practice with the Somnox 2 Breathe & Sleep Robot, which uses the power of breathing to calm the mind and prepare you for a good night’s sleep.
By simply holding the Somnox 2, you can physically feel a calm breathing rhythm. This will (unconsciously) encourage you to adopt the same soothing rhythm.
Tips for Healthy Breathing
There are several other things you can do to support healthy breathing and, consequently, a healthier you:
- Quit smoking (or don’t start if you don’t smoke). As the number one risk factor of lung cancer and other lung diseases, taking steps to quit smoking is essential.[*] Also, try your best to avoid secondhand smoke.
- Keep active. Regular aerobic exercise strengthens the lungs and keeps them healthy. Aim to get 150 minutes of aerobic exercise per week.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Being overweight increases a person’s risk of breathing difficulties.[*] In addition to exercising, maintain a nutritious diet to support a healthy weight.
- Limit exposure to air pollution. Indoor and outdoor air can contain particles and pollutants that damage your lungs. To keep your lungs healthy, maintain a clean home and stay inside on days when the outdoor air is unhealthy. You can check the outdoor air quality where you live by visiting airnow.gov.
- Practice diaphragmatic breathing exercises. Diaphragmatic breathing exercises will not only help reduce your stress, but can also help strengthen your lungs and diaphragm and make them more efficient.[*]
Breathe Better to Live Better
Breathing is a truly incredible process that we depend on for life. It brings oxygen into our bodies, expels carbon dioxide, and can even be harnessed to relieve stress, anxiety, and sleeplessness.
Breathing isn’t something we often consciously think about, but hopefully after reading this article, you have a greater appreciation for your respiratory system and a better understanding of the superpower that’s available within all of us.
For anyone looking to improve their sleep, Somnox 2 is your science-backed sleep companion that guides you towards slow-paced breathing that helps you fall asleep faster, worry less and wake up rested. 70% of our users improved their sleep quality within 4 weeks.
by Baginda Tirtadji | Monday, May 10, 2021 | Breathing, Research
Somnox’ mission is to unlock human potential by improving the sleep of 100 million people by 2030. We are continually working with sleep science experts, neuroscientists and health professionals to ensure that our products live up to this goal. In our last experiment, we investigated how the Sleep Robot supports coherent breathing to calm you down. We observed that coherent breathing exercises with the Somnox Sleep Robot before bedtime and just after waking up aligns your breathing and heart rate, and helps decrease resting heart rate, which are indicators of relaxation. More research into the effects of coherent breathing will be done in future studies.
Somnox is committed to developing products that you can trust. We continually improve our products based upon user experiences and the latest research. Sleep has a large impact on your wellbeing and it is important that we take your health seriously. Therefore, we will keep sharing our learnings with you. Wondering whether Somnox is right for you? Take our quiz and get our free advice.
What is coherent breathing?
You breathe in and breathe out, without actually thinking about it. You unconsciously inhale to let air into your lungs and oxygenate your body’s tissues. What’s unique about breathing is that you can take it under conscious control too. Coherent breathing is all about conscious, slow and rhythmic breathing. Your natural breathing rate ranges from ten to twenty breaths per minute (1). With coherent breathing, you decrease this breathing rate significantly to six breaths per minute. This has been proven to have a relaxing effect on the body and mind (2).
The effect of coherent breathing has something to do with your autonomic nervous system, which can be divided into the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system controls your stress responses (fight-or-flight) (3,4). The parasympathetic nervous system makes sure your body gets rest for restorative purposes (rest and digest) (3,4). A lower breathing rate and longer exhales lead to parasympathetic effects that initiate a relaxation response (2,5,6). Thus, slow coherent breathing transforms the body from a stressed state into a relaxed state which is favorable for a good night’s sleep (7).
Coherent breathing example: breathe in for four seconds… and breathe out for six seconds… do this breathing exercise for 10 minutes.
How is coherent breathing related to your heartbeat?
What’s interesting, is that coherent breathing impacts your heart rate. While breathing in, your heart rate goes up and while breathing out, your heart rate slightly decreases (see Figure 1 below) (8). This phenomenon is called heart coherence, and is reached during coherent breathing or when experiencing positive emotions, such as love, joy and gratitude. It’s a sign of a happy and healthy body that is resilient to stressful events that can be encountered during the day (9). 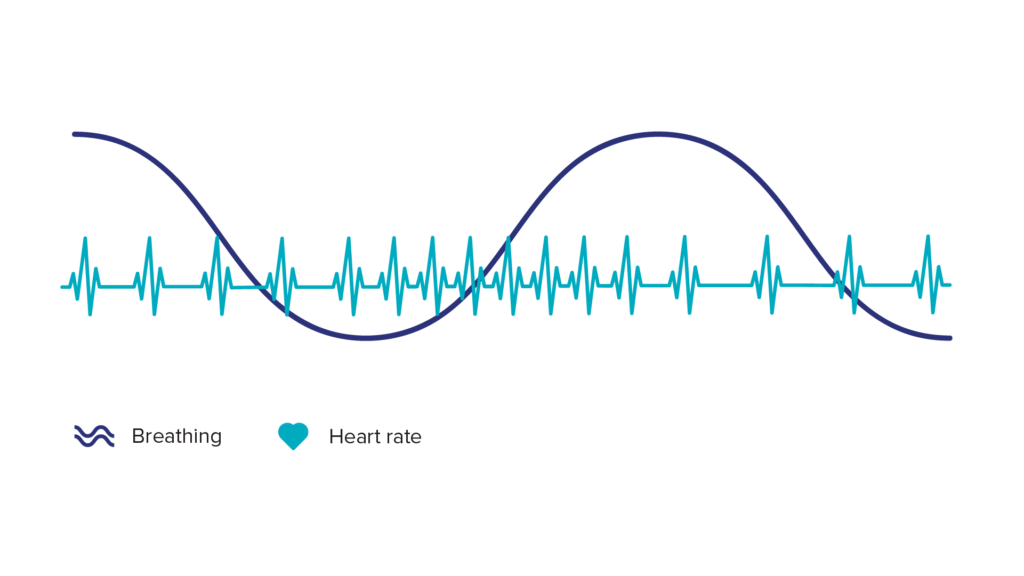
Figure 1: Heart rate goes up while breathing in and heart rate goes down while breathing out. This occurs when you practice coherent breathing and is a sign of a stress-resilient body.
How to do coherent breathing with Somnox?
Coherent breathing can relieve stress and therefore help you fall asleep more easily (9). You can use the Somnox Sleep Robot to do coherent breathing exercises (see Figure 2). We recommend performing these exercises just before going to bed for a good night’s sleep, or just after waking up to start the day peacefully.
The following settings for the Sleep Robot are recommended:
- Program: Napping
- Breathing start rate: 6 breaths per minute
- Breathing end rate: 6 breaths per minute
- Breathing duration: 10-15 minutes
- Select some soothing sounds according to your preference
You can change your breathing settings in the mobile application. More information how to do this can be found here:
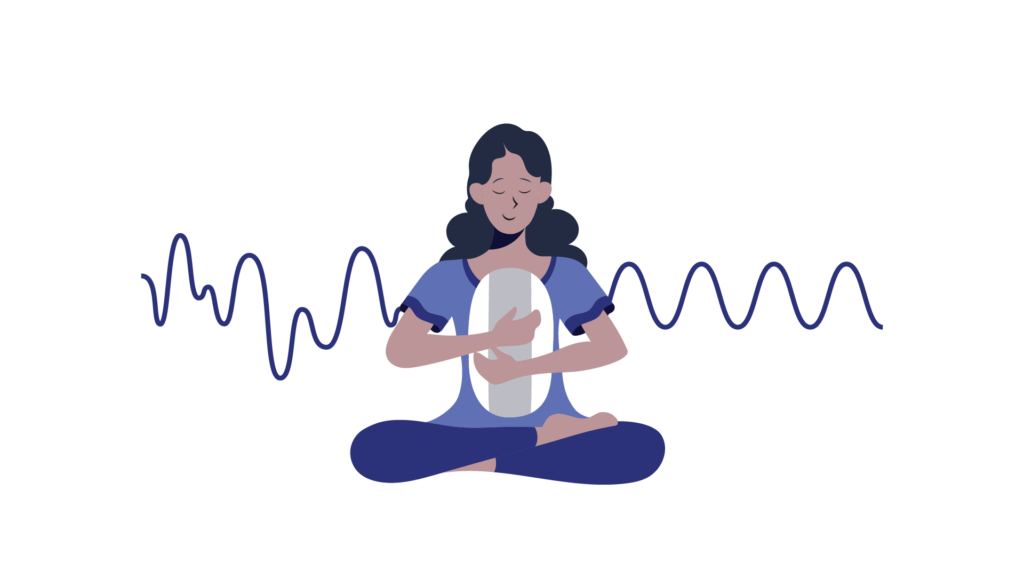
Figure 2: With the Sleep Robot, you can practice coherent breathing which consists of a regular breathing pattern and has a sinus-like effect on heart rate. This is a sign of parasympathetic dominance.
Let’s take a closer look at our experiment
The Somnox Sleep Robot is designed to let go of stress and prepare the mind for sleep with breathing exercises. After all, hyperarousal (an overactive body and mind) is a very important sleep influencing factor (10-12). Heart rate is an important measure for stress. Therefore, Somnox has investigated the effects of coherent breathing with the Sleep Robot on heart rate.
Five volunteers participated in this four-week experiment. In week one, baseline heart rate measurements were done daily in the morning. In week two, three and four, participants did coherent breathing exercises in the morning and evening while heart rate was monitored (using the PolarH10 Chest Monitor). The breathing exercises consisted of a daily 10-minute program with a breathing rate of 5 or 6 breaths per minute guided by the Somnox Sleep Robot.
Our research team has performed the data analysis and gained two important findings.
Finding (1): coherent breathing with the Sleep Robot has an effect on heart rate and leads to heart coherence
Our research team observed that coherent breathing exercises with the Sleep Robot indeed have effects on heart rate and leads to heart coherence. While breathing in, heart rate goes up and while breathing out, heart rate goes down. This is a sign of parasympathetic activity which is part of the relaxation mechanism of your body. In the video below, Julian Jagtenberg, founder of Somnox, demonstrates this phenomenon.
Finding (2): coherent breathing with the Sleep Robot can decrease resting heart rate
We also observed that coherent breathing with the Sleep Robot decreased resting heart rate over the timeframe of four weeks in three out of five participants (see Figure 3). In week one, baseline measurements were conducted. In week two, three and four, participants did coherent breathing exercises with the Sleep Robot. As you can see in Figure 3, resting heart rate decreased or stayed almost constant compared to week one. A lower resting heart rate is a sign of relaxation and overall health & wellbeing, and therefore interesting to investigate further in future experiments.
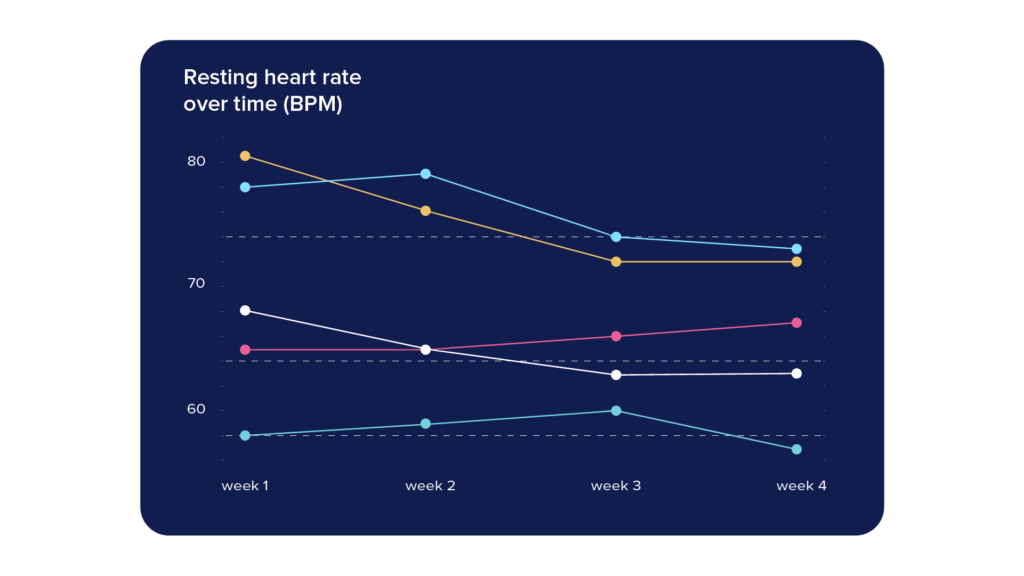
Figure 3: This graph shows the resting heart rate of participants over four weeks.
What’s next?
Stress has a large impact on your sleep. The Sleep Robot can help initiate a relaxation response with coherent breathing exercises. These exercises give you a calm mind and prepare you for bed. In our experiment, we observed effects on heart rate which is an important parameter for evaluating stress and relaxation factors. We want to keep exploring the effects of breathing exercises with the Sleep Robot on relaxation and sleep.
Somnox is committed to developing products that you can trust. We continually improve our products based upon user experiences and the latest research. Sleep has a large impact on your wellbeing and it is important that we take your health seriously. Therefore, we will keep sharing our learnings with you. Wondering whether Somnox is right for you? Take our quiz and get our free advice.
Learn more about our latest findings: https://somnox.com/blog/research-sci-somnox/
References
- Russo MA, Santarelli DM, O’Rourke D. The physiological effects of slow breathing in the healthy human. Breathe. 2017;13(4):298-309
- Lin IM, Tai LY, Fan SY. Breathing at a rate of 5.5 breaths per minute with equal inhalation-to-exhalation ratio increases heart rate variability. International Journal of Psychophysiology. 2014;91(3):206-211
- Jänig W. Autonomic Nervous System. In: Schmidt R, Thews G, ed. by. Human Physiology. 2nd ed. Berlin: Springer; 1989. P.333-370
- Buijs RM. The autonomic nervous system: a balancing act. Handb Clin Neurol. 2013;117:1- 11
- Pal GK, Velkumary S, Madanmohan. Effect of short-term practice of breathing exercises on autonomic functions in normal human volunteers. Indian J Med Res. 2004;120(2):115-21
- Sunil Naik G, Gaur G, Pal G. Effect of Modified Slow Breathing Exercise on Perceived Stress and Basal Cardiovascular Parameters. Int J Yoga. 2019;11(1):53-58
- Jerath R, Beveridge C, Barnes V. Self-regulation of breathing as an adjunctive treatment of insomnia. Front Psychiatry. 2018;9(780):1-7
- Pinsky, M., 2006. Chapter 34 – Heart–Lung Interactions. In: R. Albert, A. Slutsky, M. Ranieri and J. Takala, ed., Clinical Critical Care Medicine. [online] Mosby, pp.369-382. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323028448500391
- Steffen P, Austin T, DeBarros A, Brown T. The Impact of Resonance Frequency Breathing on Measures of Heart Rate Variability, Blood Pressure and Mood. Front Public Health. 2017;5(222):1-6









Recent Comments